Learn More About The QEEG

Brain Therapy Clinic is proud to announce that we have a new piece of brain mapping technology in the Clinic. Over the past few months, the QEEG has been put to work detecting the areas in the brain that were affected by the injury. Many people have asked us, what is a QEEG? how does it work? how can it help? what are amplitude levels?… But don’t worry, we have all the answers for you.
We will cover the most asked questions about the QEEG machine.
- What is a QEEG?
- How does it work?
- How can it help?
- What are amplitude levels?
What is a QEEG?
QEEG is short for quantitative electroencephalograms, it maps, records and indicates where brain activity has higher or lower amplitude levels. Using this data, it becomes easier to pinpoint the strengths and weaknesses after suffering a brain injury and help bring the amplitude levels back to normal.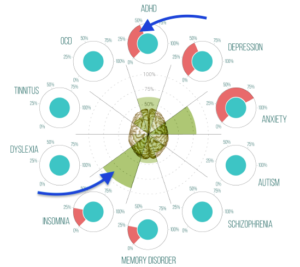
First, patients are asked a series of questions regarding the issues that they have been noticing or experiencing after the brain injury has occurred. For some patients, they have trouble sleeping, having trouble remembering things and high levels of anxiety. The recorded data indicated by the red on the graph and is compared after the QEEG testing is complete. The QEEG uses a multi-electrode cap to record and present the data in a coloured brain map showing specifically the areas where the amplitude levels are higher or lower than average shown here by the green.
The QEEG has detected a higher level of insomnia and anxiety based on brain activity during testing. Once the testing is complete, a TBI Action Plan and neurofeedback training plan will target the areas in the brain that is experiencing higher or lower amplitude levels.
How does it work?
The QEEG machine simply records your brain activity with a cap that looks very similar to a swim cap with 32 electrode points. By simply injecting the gel into each electrode point helps the QEEG machine to read and record your brains activity, these electrode points record the brain activity to help identify areas of the brain that are above or below the normal amplitude levels.
The QEEG is the initial test and takes about 20 minutes to complete, the testing is divided into two 10 minute tests. The first test is done with your eyes open for 10 minutes, this test is recording the Delta amplitude levels in your brain. The Delta activity in your brain is extremely sensitive to eye blinks and eye movements which results in high frontal Delta amplitude levels. The second test is done with your eyes closed, this test is recording Alpha amplitude levels and other activity in your brain.
In order to help your brain heal, you need to know what areas of the brain are affected the most.
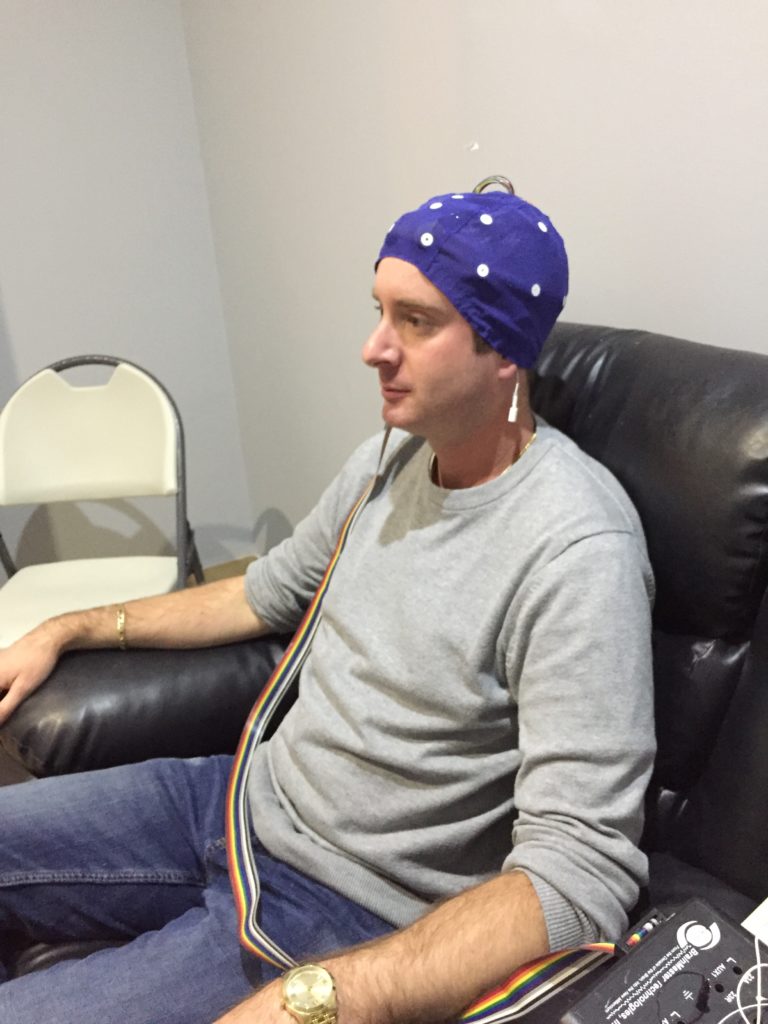
After the initial QEEG testing and report, you can now begin to start your TBI Action Plan with neurofeedback.
The neurofeedback helps train the brain and help bring back normal amplitude levels, this process takes about 10-20 minutes each session.
The QEEG is the beginning of the healing process and the start if making a TBI Action Plan to help you get back to your daily life.
How does it help?
Brain injuries are common, however, they are not always easiest to treat. When a brain injury has occurred the sensories in your brain that indicate where some abnormalities are. For example, the excess Theta and Alpha, as well as deviant Beta power, have been associated with ADHD. The excess Delta power has been associated with traumatic brain injuries and memory disorder. These high levels can also explain and be related to sleep, anxiety and attention issues.
Using the QEEG machine, we can better pinpoint areas in the brain where it is producing higher or lower levels of Theta, Alpha, Beta and Delta and create a TBI Action Plan. The TBI Action Plan is a plan created for specific areas that are producing higher or lower levels, this would result in counteract the levels and help them return to normal levels.
What are amplitude levels?
Delta
The amplitude of Delta activity was high at central electrode sites. High Delta power is associated with impaired memory and traumatic brain injuries. Delta is dominant during deep sleep and is associated with low arousal during wakefulness.
THETA
The amplitude of Theta activity was high at central sites.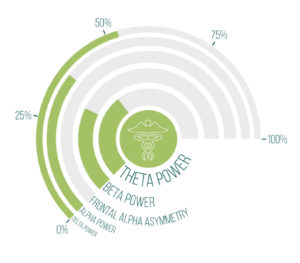
The most reliable EEG biomarker for attentional disorders is the presence of excessive front-central. Theta power, reflecting a hypo-arousal in those areas resulting in sub-optimal functioning of brain areas that are important for the regulation of attention and emotions, impulse control and planning.
ALPHA
The ‘Alpha Arrest Reaction (ARR)’ was not clearly present at central electrode sites. This is caused by an absence of dominant Alpha activity during the Eyes Closed condition and the presence of dominant Alpha activity during the Eyes Open condition.
SMR or Sensory- Motor Rythm
Slow Beta activity on central brain areas is called ‘Sensory-Motor Rythm’ (SMR). Spindling SMR activity during sleep is important for deep sleep. Its role is to inhibit motor output excessive SMR during wakefulness can be a sign of hypo-arousal and impaired vigilance regulation and has been associated with attentional disorders.
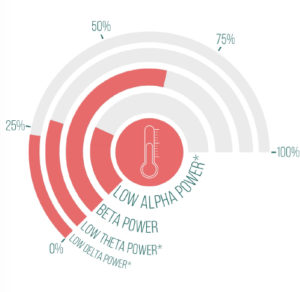 BETA
BETA
The patient showed high Beta activity at frontal sites.
A deficit in Beta activity has been linked with attentional disorders and often coincides with high Theta power. However, about 15% of the patients with attentional disorders will show excessive Beta. Excessive Beta amplitudes are associated with hyperarousal and can be also associated with anxiety disorder and insomnia. Beta amplitudes are very susceptible to muscle artifacts: Excessive Beta in frontal, temporal and occipital Beta can be caused by tension in the forehead (e.g. frowning or raised eyebrows), jaw muscles and neck muscles, respectively.

